Nanotechnology has been around for years but never have we had the technology to keep up with it. Finally, in the past couple decades; scientists have created microscopes allowing us to see the once-invisible world. Some of these instruments include the popular light microscope, the transmission electron microscope (TEM), and the scanning electron microscope (SEM). Now that we can see into the nano world, scientists have begun to actually apply nanotechnology to practical and everyday concepts. Besides the many trivial applications for nanotechnology, such as nano silver socks, there are a few potential major breakthroughs; one being Nanomedicine. Nanomedicine according to Robert Freitas, is the monitoring, repair, construction and control of human biological systems at the molecular level, using engineered nanodevices and nanostructures. In his fascinating lecture, Professor Leonard Rome categorized the uses of nanotechnology in the body under one of these three groups: tools for disease diagnosis, new biological materials, and creation of new drugs and drug delivery systems. His ideas for tools for disease diagnosis included devices the size of iPods to analyze human blood. Interestingly enough, similar devices have already b een introduced such as some diabetes monitors.
een introduced such as some diabetes monitors.
As for biological methods, some kinds of nanobots are being used as identifiers to gain a greater understanding of the human body. Also, Professor Carlo Montemagno introduced the idea of powering nanodevices with biological cells. The idea that mechanical machines and biological life could be manipulated to work as one, fascinated me.
Lastly, for drug deliver systems; structures called vaults are being created to either be a transporter, regulator, or protector within the human body. These vaults are made of a major vault pr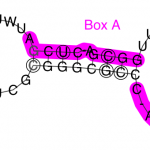 otein (MVP), two smaller proteins, TEP1 and VPARP, and lastly a small RNA called vault RNA. These vaults have been injected with drugs successfully but the last thing that needs to be addressed is how to target vaults. Some ideas include therapeutics, non-machines, controlled release, or biological sensors.
otein (MVP), two smaller proteins, TEP1 and VPARP, and lastly a small RNA called vault RNA. These vaults have been injected with drugs successfully but the last thing that needs to be addressed is how to target vaults. Some ideas include therapeutics, non-machines, controlled release, or biological sensors.
http://www.foresight.org/Nanomedicine/
http://www.vaults.arc.ucla.edu/
http://www.nanomedjournal.com/
http://nanobot.blogspot.com/2004/02/amazing-montemagno.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19206245
-
Pages
-
Categories
-
Archives